Schedule Your Consultation Today - Contact Us
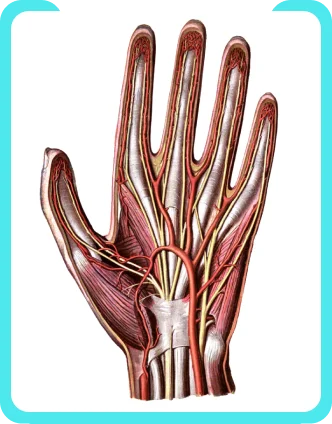
The wrist links the hand to the forearm. The wrist is a complex system of many small bones (known as the carpal bones) and ligaments. The carpal bones are arranged in 2 interrelated rows. One row connects with the ends of the bones in the forearm—the radius and ulna. If you hold your hand in the thumbs-up position, the bone on the top of your forearm is the radius; the one on the bottom is the ulna.
The other row of carpal bones connects with the bones of the palm of the hand. There are synovial joints between the carpal bones in the wrist. The joint surfaces, where the bones meet, are covered with articular cartilage. Articular cartilage is smooth and slick, which enables very smooth and pain-free motion.
The hand is made up of many bones:
The muscles in the forearm and palm (thenar muscles) all work together to keep the wrist and hand moving, stable, and well-aligned. The image shows the bones of the hand from the back side. The red lines show where the tendons attach the muscles to the bones.
Many of the muscles that move the fingers and thumb originate in the forearm. Long flexor tendons extend from the forearm muscles through the wrist and attach to the small bones of the fingers and thumb. When you bend or straighten your fingers, these flexor tendons slide through snug tunnels, called tendon sheaths, that keep the tendons in place next to their respective bones. Within this sheath, a slippery coating called tenosynovium surrounds the tendons, and keeps the tendons moving smoothly under the ligaments when the hand is in motion.
Tendons are white, flexible rope-like cords at the ends of muscles that attach muscles to bone. When muscles contract, they pull on the tendons to move the bones. The tendons that run down our fingers are held in place by a series of ligaments, called pulleys, that form stable arches over tendons, forming a “tunnel-like” sheath. Normally, the tendons glide easily through the tunnel.
Ligaments of the back of the hand;
There are many ligament of the hand that are made up of tough bands of fibrous tissue. As there are many small bones and joints in the hand, there are also many ligaments within the hand that help to keep the bones together and stabilize the hand.
Other stabilizers in the hand include the joint capsules, which are also made up of fibrous connective tissue that surround each of the joints. Synovial membranes line the inner aspects of the joint capsules and produce synovial fluid to lubricate all the joints.
The median, radial, and ulnar nerves are the three major nerves that run the length of the entire arm. These nerves control the muscles of the forearm and hand and give us the sensations of touch, temperature, and pain.